Back
Rizal Shrine Intramuros- Energy Efficiency
Year: 2022
Category: Cultural Architecture
Skills: Revit, Insight
The negative effects of rapid climate change continue to challenge us to find ways to be more energy-efficient. As one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, the building industry has a responsibility to reduce energy consumption in the built environment. However, heritage buildings have often been excluded from the discourse on energy efficiency due to their specific conservation needs. As a result, this study aims to develop a framework for assessing and recommending energy-saving measures for heritage structures.
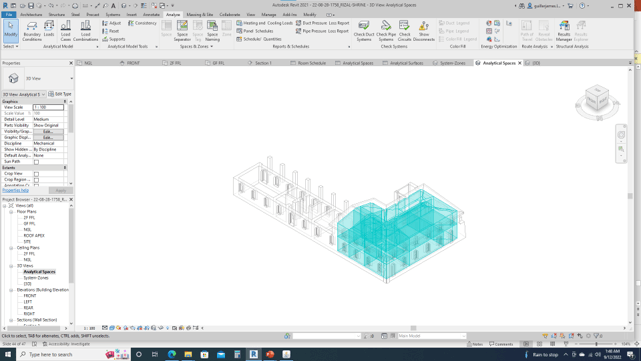
The proposed framework will utilize a Cultural Stepped Strategy Framework, which involves an assessment of the heritage building's cultural significance as the first step. The second step involves an examination of the local climate and the building's current energy consumption. Following this, an energy model will be developed through Autodesk Revit, and various scenarios will be created through Autodesk Insight to show the relationships between different scenarios and the building's energy performance. Additionally, we will assess which scenario from Autodesk Insight and which design guideline from Climate Consultant is acceptable and will not negatively impact the heritage building's cultural significance.
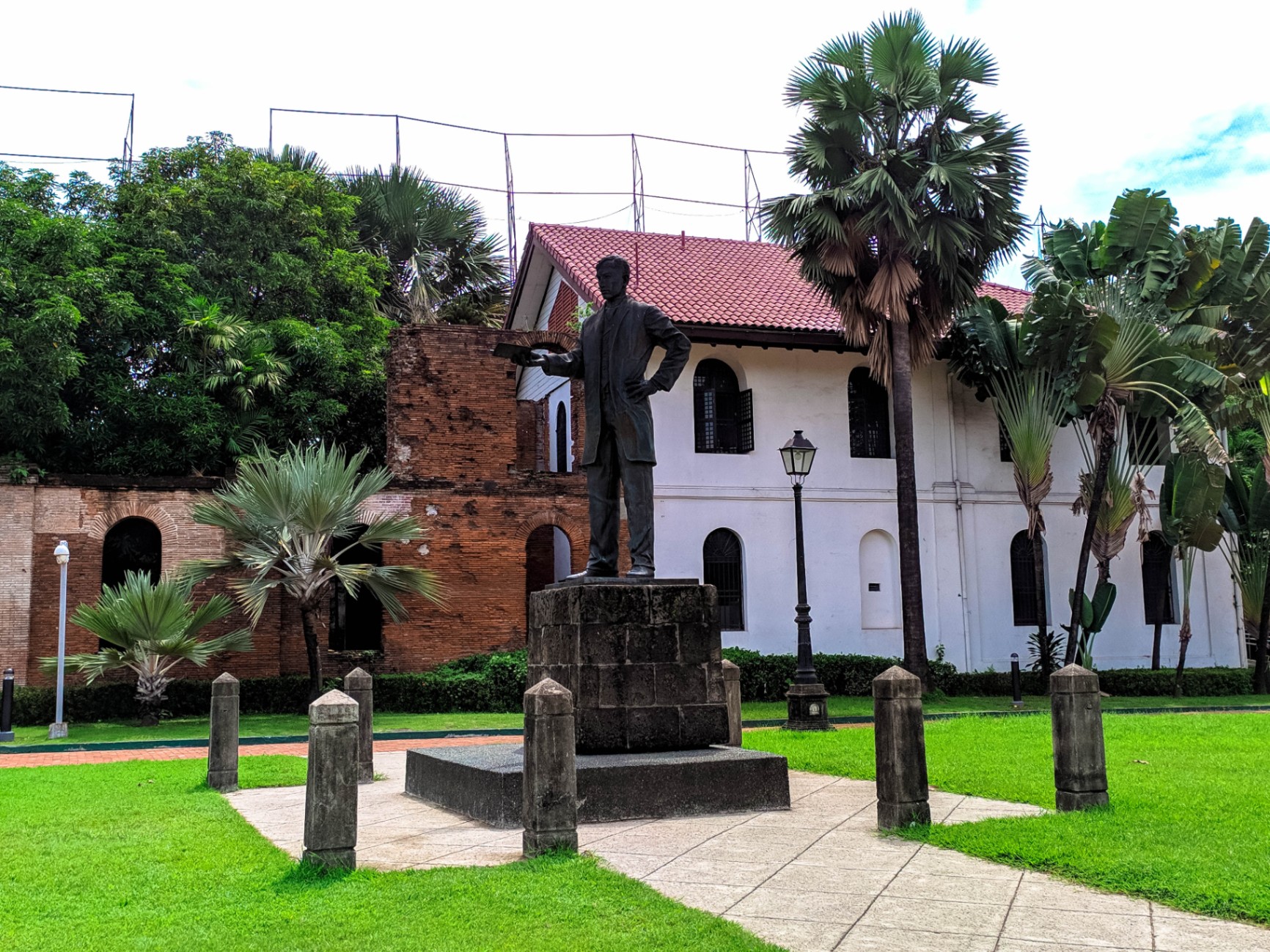
The Rizal Shrine in Fort Santiago, Intramuros, will be used as a case study to develop and test this framework. The Shrine's cultural significance will be assessed using the Burra Charter, and its energy consumption will be examined. Furthermore, different scenarios will be created through Autodesk Insight to show the relationships between various scenarios and the building's energy performance. We will analyze the quantitative and qualitative data against the Rizal Shrine's cultural significance to determine the best energy efficiency solution for the site.
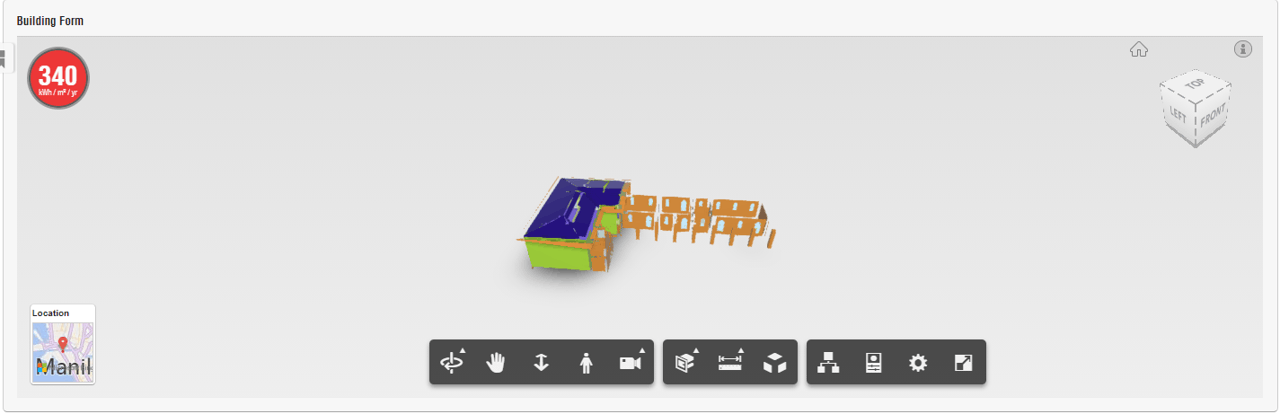
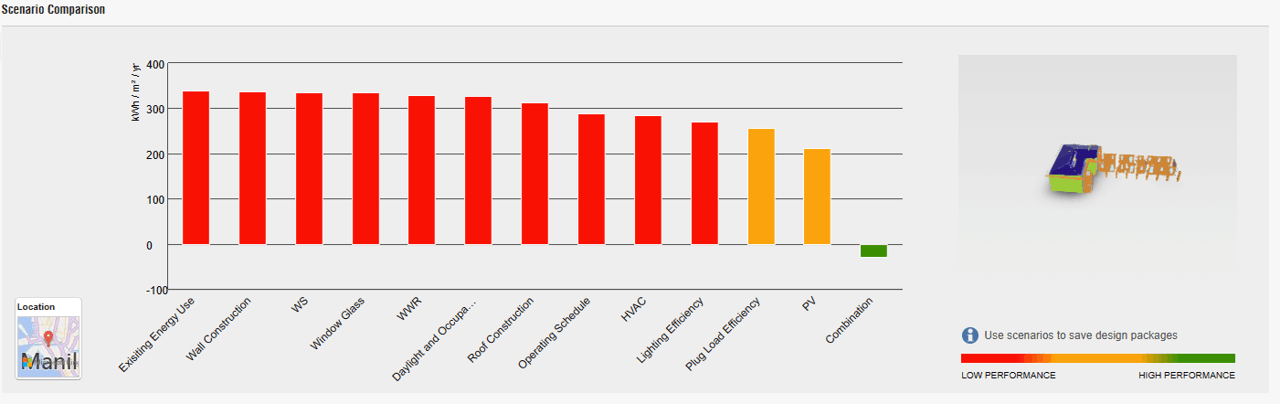
The partial conclusion reveals that the Rizal Shrine's historical value is of primary significance. As for the simulation results, they show that the site is not energy-efficient and does not meet the Architecture 2030 standards. To employ the Climate Consultant program criteria for heritage structures, we must study how they are set for a new type of development.
To determine the best energy efficiency solution for the Rizal Shrine, we will use two methods. The first involves creating scenarios for the site's energy use. The second involves analyzing the quantitative and qualitative data against the Rizal Shrine's cultural significance. By combining these methods, we will determine the best course of action to make the Rizal Shrine more energy-efficient while preserving its cultural significance.
In conclusion, this study proposes a framework for assessing and recommending energy-saving measures for heritage structures that balances energy efficiency with the preservation of cultural significance. The Cultural Stepped Strategy Framework is utilized to assess cultural significance, examine local climate and energy consumption, and develop and test energy efficiency scenarios. By applying this framework to the Rizal Shrine, we will determine the best energy efficiency solution that does not compromise the heritage building's cultural significance.
Guiller James Lopez
More by Guiller James Lopez
View profile